Change Management Fundamentals Training: What You Need to Know to Get Started
Change is no longer a rare event. From digital transformation to cultural shifts, mergers and acquisitions to ERP and CRM rollouts, today’s organizations face constant disruption. Yet despite the investment, most transformation initiatives struggle. Research consistently shows that up to 70% of change efforts fail to achieve their intended outcomes.
Why? Because too often, leaders focus on the technical side of change — processes, systems, structures — while underestimating the human side of change. Employees feel uncertain, resistant, or unprepared. Leaders fail to model the right behaviors. Communication is inconsistent. And without adoption, even the best-designed initiatives fall flat.
That’s where change management fundamentals come in. Whether you are a new practitioner, a project manager, or a leader supporting change, understanding the basics of change management is critical to success. This article provides a training-style overview of what you need to know to get started.
Let’s get started
Watch this video:
or
read the guide below.
Repeatable 360° Change Management Framework
What Is Change Management?
At its core, change management is the implementation, control, and stabilization of an organization’s change process. But unlike project management, which focuses on technical tasks and deliverables, change management focuses on people and feelings.
It is a structured approach to helping individuals and teams transition from a current state to a desired future state. That includes:
Preparing people for the change.
Equipping them with the tools and knowledge they need.
Supporting them through resistance.
Reinforcing new ways of working until they become the norm.
A simple way to think about it: Project management delivers the solution. Change management ensures people adopt it.
Why Change Management Is Essential
Without change management, projects risk becoming “technical successes but human failures.” The system goes live, the process is rolled out, but employees don’t adopt it. The result: lost productivity, wasted investment, and missed business value.
Key reasons why change management is essential include:
Reducing resistance: Employees naturally resist change due to fear, uncertainty, or loss of control. Structured change management helps address those concerns.
Improving adoption: People need training, communication, and reinforcement to embrace new ways of working.
Protecting ROI: Organizations invest heavily in technology and transformation. Without adoption, the benefits don’t materialize.
Building resilience: With repeated exposure to well-managed change, organizations become more adaptable to future disruptions.
The Human Side of Change
One of the most important fundamentals is recognizing that change is emotional, not just operational. People experience a range of reactions, including:
Shock and denial: At first, people may downplay or ignore the change.
Resistance: Fear, anger, or frustration often surface as people feel disrupted.
Exploration: As information and support increase, employees begin to explore what the change means.
Commitment: Over time, with reinforcement and success, new behaviors become the norm.
Understanding this curve helps leaders and practitioners design communications, training, and support that meet people where they are emotionally.
Core Principles of Change Management
Change management fundamentals rest on several key principles:
Leadership and Sponsorship Are Critical
Change starts at the top. Leaders must model desired behaviors, actively sponsor initiatives, and communicate consistently. Employees watch leaders to determine if the change is truly important.Communication Must Be Clear and Ongoing
Effective communication is not one-and-done. It should be tailored to different audiences, delivered through trusted channels, and repeated throughout the project.Training and Enablement Build Confidence
People need practical tools to adopt change. Training sessions, guides, FAQs, and digital adoption tools help employees feel capable and supported.Resistance Is Natural and Manageable
Resistance isn’t failure — it’s feedback. By listening to concerns, addressing risks, and engaging with resistant groups, change managers can turn opposition into support.Reinforcement Ensures Sustainability
Without reinforcement, people often revert to old habits. Recognition, celebration, and ongoing support lock in adoption and drive long-term value.

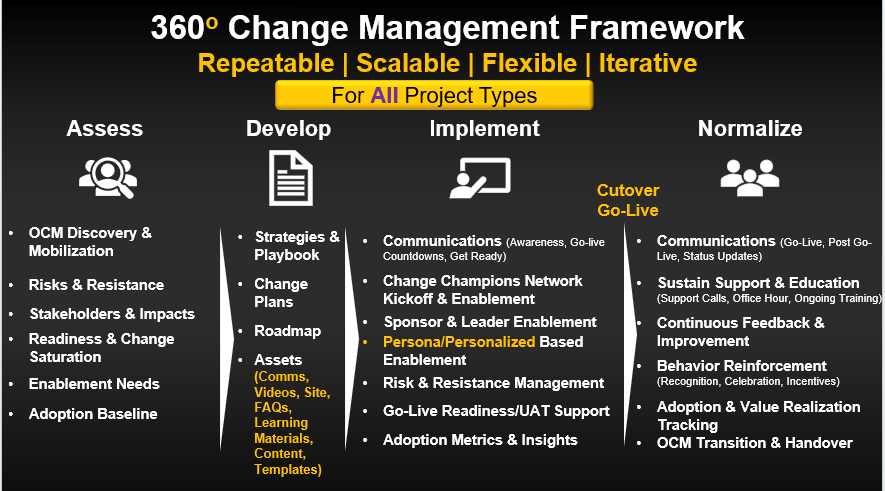
The Repeatable 360° Change Management Framework
Once you understand the fundamentals, you need a structured methodology to put them into practice. One proven model is the Repeatable 360° Change Management Framework, which provides a complete lifecycle for managing change.
The framework consists of four phases: Assess, Develop, Implement, and Normalize.
1. Assess
The Assess phase establishes the foundation. This includes mobilizing the OCM team, analyzing risks, mapping stakeholders, and assessing readiness. The goal is to understand the current state and identify barriers before they derail adoption.
2. Develop
Develop focuses on planning. Here, the OCM team builds strategies, playbooks, and detailed plans for communications, training, and engagement. The roadmap aligns OCM activities with project milestones, and governance alignment ensures change management is embedded in delivery.
3. Implement
This is where change comes to life. Communications, leader enablement, champion networks, and user training are executed. Resistance and risks are managed in real time. Adoption metrics and insights are tracked to measure progress and adjust strategies.
4. Normalize
Too many projects stop at go-live. Normalize ensures adoption is sustained through reinforcement, feedback, and ongoing support. Adoption is measured, value realization is tracked, and OCM responsibilities are handed off to business-as-usual teams.
How to Get Started with Change Management
If you are new to change management, here are practical steps to begin applying the fundamentals:
Learn the Basics of Stakeholder Analysis
Identify who is impacted by a change and how. This helps you prioritize communication and support.Draft a Simple Communication Plan
Define what messages need to be delivered, to whom, when, and how. Even a basic plan creates clarity.Start Measuring Adoption
Track metrics such as training completion, system usage, or survey feedback. Establishing a baseline is better than guessing.Engage Leaders Early
Coach leaders on their role in sponsoring change. Provide them with talking points or toolkits to reinforce their visibility.Anticipate Resistance
Create a safe space for employees to voice concerns. Treat resistance as valuable feedback that can inform adjustments.Reinforce Success
Celebrate early wins. Recognize teams or individuals who embrace the change. Reinforcement builds momentum.
Real-World Examples of Change Management Fundamentals in Action
ERP Implementation: Without OCM, employees might resist using the new system and revert to spreadsheets. Fundamentals like stakeholder mapping, training, and reinforcement ensure adoption.
Digital Transformation: Employees may fear AI tools will replace their jobs. Clear communication and leader sponsorship help address fears and highlight benefits.
Culture Change: Shifting toward a culture of collaboration requires leaders to model behaviors, champions to reinforce them, and reinforcement to make it stick.
M&A Integration: Employees from both organizations may feel uncertain. Communication, readiness assessments, and resistance management reduce anxiety and improve alignment.
Benefits of Mastering the Fundamentals
By applying the fundamentals, organizations can:
Increase adoption and reduce resistance.
Deliver higher ROI on transformation investments.
Improve employee engagement and morale.
Build a culture of resilience and adaptability.
Establish a foundation for more advanced OCM practices.
Conclusion
Change management fundamentals are not optional — they are the foundation of successful transformation. By focusing on people, not just processes, organizations can reduce resistance, build confidence, and achieve adoption that delivers real business value.
For beginners, the most important step is to start simple: map stakeholders, communicate clearly, support users, and reinforce success. Over time, layering in a structured framework like the Repeatable 360° Change Management Framework ensures consistency and scalability.
When change becomes a discipline rather than an afterthought, organizations stop fearing disruption — and start thriving through it.
FAQ: Change Management Fundamentals
The fundamentals include leadership sponsorship, clear communication, training and enablement, resistance management, and reinforcement.
It ensures people adopt and sustain new systems or processes, protecting ROI and delivering business outcomes.
Project management delivers the technical solution, while change management ensures people adopt and use it effectively.
Begin with stakeholder analysis, communication planning, and adoption measurement. Free checklists and toolkits can help.
The Repeatable 360° Change Management Framework provides a structured, end-to-end lifecycle for adoption and sustainment.What are the fundamentals of change management?
Why is change management important?
What’s the difference between project management and change management?
How do I start learning change management?
What framework should I use for change management?
